If a merchant suspects the chargeback isn’t a genuine one, they have the option to fight back. However, chargeback fraud can be a lengthy and complicated process, leading to more issues than benefits. That’s why some businesses ultimately decide to pay out the chargeback instead.
And let’s not forget the damaged reputation, transaction processing costs, lost shipping, and overall costly fees linked to the fraudulent disputes. So, what exactly can you do to combat chargeback fraud? Tag along and find out.
What are Chargebacks?
Chargebacks are reversals of credit or debit card transactions that the cardholders’ bank initiates following their disputes of charges on their bank accounts. That means the customer’s credit card company or bank must refund the disputed amount to the customer and debit the same amount from the business’s account. This makes chargebacks appealing to bad actors who want to receive refunds and keep their purchased items.
What is Chargeback Fraud?
Chargeback fraud, alternatively referred to as friendly fraud, is the process when a consumer uses their own credit card for an online shopping transaction and later asks the issuing bank for a chargeback after already receiving the purchased goods or services. Chargeback fraud occurs when a customer deliberately disputes a charge to obtain a refund.
It can happen for various reasons, usually due to customers:
- Falsely claiming that they didn’t place the order.
- At the same time, chargebacks can be legitimately submitted in several situations. The Fair Credit Billing Act (FCBA) provides support to customers in disputes with creditors, including cases of billing errors, charges for undelivered goods, and unauthorized charges.
For businesses, chargeback fraud can lead to certain risks, including financial losses, harmed reputation, loss of customers, increased fees from payment processors, and even potential loss of the ability to accept credit card payments.
Examples of Chargeback Fraud
Chargeback fraud is damaging for the business because it essentially results in the fraudster obtaining the product or service for free or at a significantly reduced cost while the merchant suffers a financial loss.
Here are some examples of chargeback fraud to understand the potential damage caused by different types of chargebacks:
1. Friendly Fraud
For example, a customer purchases a laptop online but later claims to their credit card company that they never received the item. The customer disputes the charge, and the card issuer issues a chargeback, refunding the customer’s money. However, the customer actually received the device and deliberately filed the chargeback to avoid paying for it.
2. Card Testing
Fraudsters often engage in card testing to verify the validity of stolen credit card information. They make small purchases from different online merchants to test if the card details are functional. Once they find a working card, they often proceed to use it for bigger purchases and file chargebacks in order to avoid detection.
3. Exploiting Return Policies
For instance, a fraudulent customer buys expensive clothing from an e-commerce store and wears it for a special occasion. After the event, they send back the items, claiming they were never worn and were unsatisfactory. The merchant processes the refund, but the customer has essentially used the clothing for free through the chargeback process.
4. Online Shoplifting
This happens when an individual downloads digital content, such as software or e-books, from an online store. They then dispute the charge, alleging they never received the items or that they were defective. The chargeback is granted, allowing the fraudster to enjoy the digital content without paying for it.
📎 Related: Fraud Detection — What You Need to Know in 2024
What is the Process of an E-Commerce Chargeback?
An e-commerce chargeback occurs when customers dispute a specific transaction with their bank or credit card issuer. Once the customer initiates a chargeback, the bank automatically reverses the transaction and deducts the funds from your merchant account.
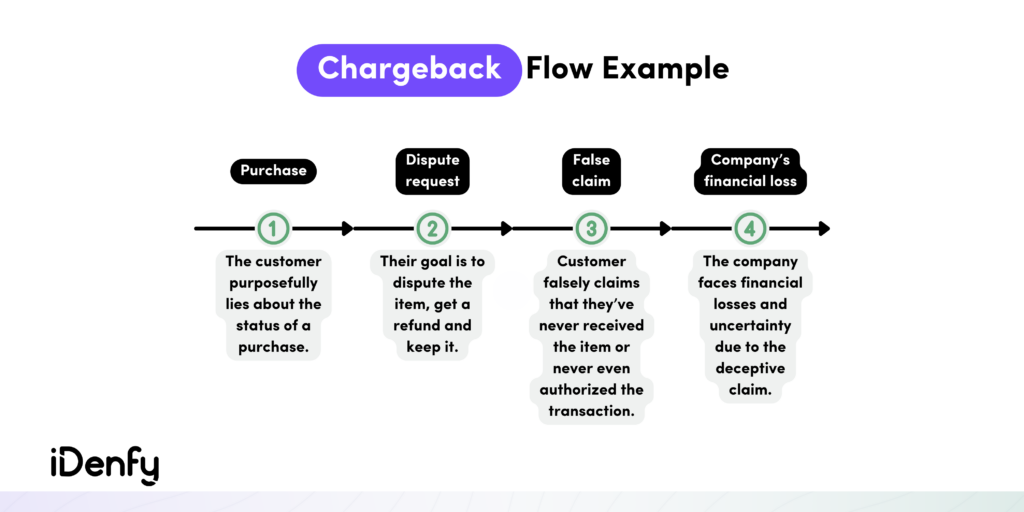
Typically, an e-commerce chargeback involves the merchant, cardholder, and the issuer or the bank. The process looks like this:
- The chargeback is initiated. The company receives a notification from the payment processor or bank indicating the deduction of funds from their account, along with a chargeback reason code (transactions made with a stolen card, undelivered orders, wrong products, or items not as described), detailing the customer’s complaint. Additionally, a chargeback process fee may be levied on the company.
- The chargeback needs to be addressed. The company is required to gather and submit compelling evidence, such as order documents, delivery confirmation, or customer communication, to prove that the transaction was valid and the chargeback is unwarranted. The company must respond within a specific timeframe, known as the chargeback response time limit, to avoid losing the disputed funds and facing additional penalties.
What is a Chargeback Reason Code?
If a customer makes a purchase with their credit card and then, later on, disputes the charge with the bank, then the bank uses something called a chargeback “reason code.” It’s like a mix of numbers and letters that tells the merchant why the customer’s disputing the charge.
Different credit card brands, like Visa and Mastercard, have their own set of these reason codes. They’re important because they help merchants figure out why chargebacks happen frequently, and they can also detect fraudulent chargebacks.
Legitimate Chargebacks vs Fraudulent Chargebacks
The main difference is that a legitimate chargeback occurs when a cardholder disputes a transaction that is genuinely unauthorized or defective, while a fraudulent chargeback happens when a cardholder falsely claims a transaction as unauthorized to obtain a refund and keep the purchased goods or services.
Before claiming any chargeback is fraudulent, companies must consider that proving chargeback fraud requires time and effort. According to the FCBA, customers have a 60-day period to dispute unauthorized or incorrect charges in writing.
Similarly, the Electronic Funds Transfer Act (EFTA) offers comparable protections for unauthorized Electronic Funds Transfers (EFTs) in bank and debit accounts. To qualify under the EFTA, the transaction must meet certain criteria, such as being made by someone without authority to do so, being of no benefit to the customer, or not having been made by the customer.
How Does Chargeback Fraud Affect Businesses?
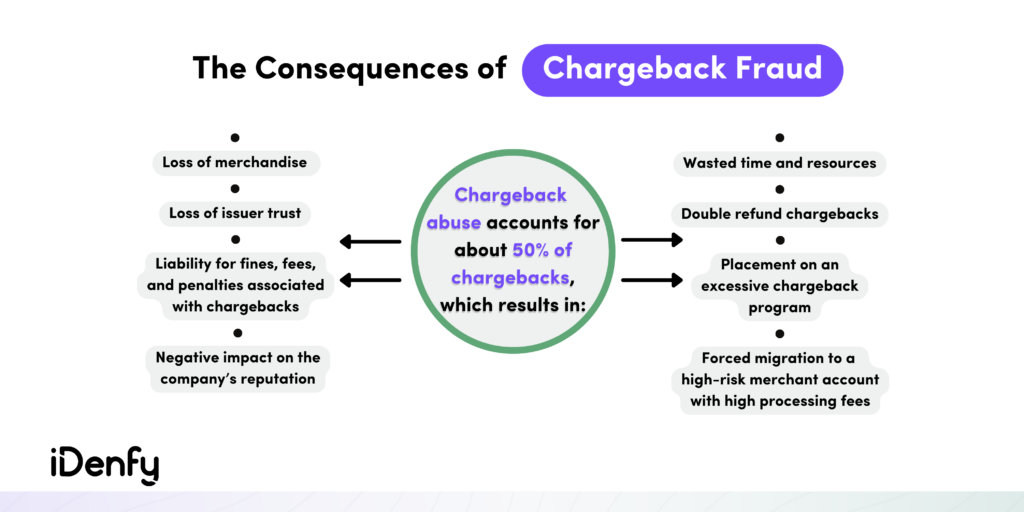
Up to $50 per chargeback doesn’t sound so bad? Well, it’s not only that but the fact that chargebacks can lead to severe business losses, including long-term consequences. This is why paying for each chargeback results in both lost operational costs and potential fines for penalties, further impacting the business.
Over time, as chargeback rates rise beyond a certain threshold, a merchant’s credit card network may enroll them in an excessive chargeback program, leading to substantial fines. Additionally, the merchant might be compelled to switch to a high-risk merchant account, incurring high processing fees.
Double refund chargebacks are also a huge concern for businesses. These happen when a customer initiates a chargeback while, at the same time, requesting a refund. In some cases, merchants can unknowingly process the refund before even being aware of the customer’s chargeback, resulting in businesses paying twice for the same transactions.
What Businesses are More Susceptible to Chargeback Fraud?
Ufortunately, chargeback fraud poses a risk to any business that’s operating online. That’s why any business processing credit card transactions should be vigilant against chargeback fraud. However, certain companies are more likely to experience this type of fraud:
- Online retailers and service providers. Digital products, like mobile games or online courses, are especially prone to chargeback fraud, as customers can easily lie about not liking the quality of service.
- Subscription-based businesses. For example, subscription boxes or streaming services. Customers may forget their subscriptions, fail to recognize recurring charges, or mistakenly dispute charges.
- Businesses dealing in high-value products or services, such as luxury goods or travel accommodations, are particularly vulnerable. The allure of obtaining expensive items or services without payment can make these businesses attractive targets for fraudulent chargeback claims.
How Can Companies Detect and Prevent Chargeback Fraud?
The chargeback dispute process requires significant time and resources for businesses. Consequently, preventing chargeback fraud successfully means that businesses must build a strong risk assessment management system consisting of different processes. Customer screening, ongoing monitoring, and authentication measures are just the beginning of a chargeback fraud prevention program.
While some businesses often choose not to dispute fraudulent chargebacks due to the effort and cost being not worthwhile, we recommend looking at some tools and processes that will help prevent chargeback fraud:
1. Have Clear Cancellation and Return Policies
Always ensure that your customers are well-informed about the process to cancel or return their orders if they decide to do so. This will significantly improve their overall experience. Ambiguity around subscription opt-outs typically leads to numerous chargebacks. By providing clear and accessible cancellation and return procedures, you can effectively reduce chargebacks and enhance customer satisfaction.
2. Detect Fraudsters Easier with Identity Verification
Businesses and e-commerce platforms can implement identity verification methods such as two-factor authentication or phone number verification before allowing users to make purchases. This helps confirm the legitimacy of the customers and reduces the risk of chargeback fraud.
However, the safest measure is document verification, where the customer is asked to upload their government-issued ID document. By verifying the identities of customers during the onboarding process, businesses can ensure that the customers conducting transactions are genuine and not using stolen or fraudulent identities. This helps in reducing the chances of fraudulent chargebacks resulting from unauthorized transactions.
3. Implement Monitoring to Recognize Fraud at Any Stage
There’s no doubt that artificial intelligence can process large amounts of data and identify subtle red flags that might go unnoticed. AI-enabled monitoring systems conduct continuous analysis of customer transactions and behavior patterns. By tracking and analyzing transactional data over time, businesses can identify suspicious activities, including patterns consistent with chargeback fraud.
Let’s say a customer makes multiple high-value purchases within a short period and then disputes all those transactions as fraudulent. A monitoring system would flag this as suspicious behavior, as it may indicate an attempt to exploit the chargeback process for financial gain. Monitoring also helps maintain customer profiles with data such as transaction history, geolocation, and spending habits. By cross-referencing this information with chargeback claims, businesses can spot discrepancies more easily.
4. Stay Compliant with Payment Processing Rules
To ensure clarity and prevent chargebacks, it’s crucial to set standard security protocols for card transactions and keep records of customer transaction data. Collecting detailed information for each order will help prove the authenticity of transactions and provide compelling evidence in case of any chargeback disputes. For example, records of delivery services help businesses contest chargebacks where customers falsely claim they didn’t receive the goods or services.
Payment processors also offer chargeback prevention programs or tools to businesses that comply with their rules. These programs often include fraud detection measures that can help businesses identify and prevent fraudulent transactions.
How iDenfy Can Help Reduce Your Chargeback Rate
If you don’t know where to start, iDenfy’s fraud prevention and identity verification solutions can help prevent chargeback fraud in a simple, efficient, and compliant manner.
Try out our tools for free today, or see our success stories from partners using our identity verification, KYB, or AML tools.




