Technology has transformed the way businesses operate. It plays a significant role in helping them understand customers’ needs, target potential customers, and improve operations. Unfortunately, technology has also brought many threats to businesses. One of the common ones is identity theft. Nowadays, cybercriminals are using technology to perform identity theft.
In fact, identity theft has turned into the fastest-growing crime, causing substantial financial loss to businesses across the globe. That explains why the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) alone received a staggering 2.1 million fraud reports in one year’s time.
So, tag along and allow this post to guide you through the common types of identity theft and solutions to stop them.
What is Identity Theft?
Identity theft is a deceptive exploitation of someone else’s personal information and name for personal benefit. It happens when a fraudster steals your identity and gains access to your personally identifiable information (PII) to commit fraud.
The type of sensitive information stolen by fraudsters to commit fraud may include the date of birth, address, driver’s license, bank account details, passwords, social security number (SSN), etc.
📝 Key Identity Theft Statistics for 2024
- According to the FBI, over 100,000 identity theft and personal data breaches occur every year.
- Almost one-third of Americans have been a victim of identity theft.
- Identity theft victims in the US are most commonly aged between 30-39 years old.
- Around 40% of consumers worldwide are targeted by ID theft at least once.
- Javelin Research concluded that fraudsters are quick in their efforts to take over accounts. One report revealed that 40% of account takeovers happen within 24 hours of a fraudster accessing a victim’s account.
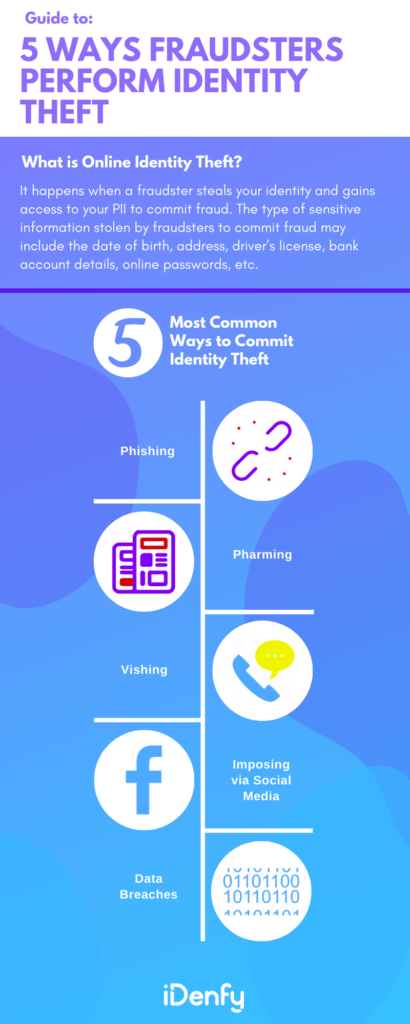
Common Tactics Criminals Use for Identity Theft
Identity theft can affect people badly. Financial setbacks, decreased credit scores, and anxiety about future financial security are just the beginning. However, staying informed about the risks of identity theft helps you safeguard yourself and your family, allowing you to enjoy modern technology’s benefits fully.
Identity theft has become increasingly sophisticated, with criminals using various complex methods to steal personal information. Some common ways to commit identity theft include:
- Completing change-of-address forms to redirect mail, which often contains personal and financial information.
- Using electronic devices attached to ATMs to “skim” information stored on credit or debit cards’ magnetic strips.
- Employing phishing tactics, such as fake emails, text messages, and websites, designed to deceive individuals into divulging sensitive information.
- Purchasing personal data from insiders, such as company employees, with access to financial information.
- Stealing electronic records through data breaches or buying credentials on the dark web.
In the following section, we’ll explore the different types of identity theft in more detail.
1. Phishing
Phishing is a method where scammers send deceptive emails that appear genuine, such as an email from your bank requesting you to confirm your account details. Criminals have also adopted a technique called SMiShing, which involves sending fraudulent text messages. SMiShing is similar to phishing, where you might receive a deceptive text message asking you to verify a purchase or account information.
As per ConsumerAffairs, phishing via voicemails, texts, and emails is one of the most common ways cybercriminals commit identity-related fraud. As soon as a recipient clicks on a malicious link, the malware starts getting installed in the background, resulting in the system freezing and revealing sensitive information.
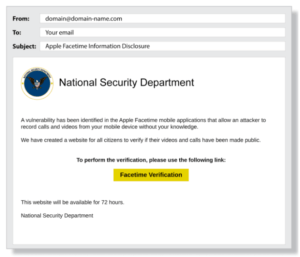
In the above example, the fraudster is pretending to be a representative of the National Security Department. The email asks the recipient to click on the link to perform a verification. As soon as the recipient clicks on the link, a malicious script will activate in the background and give the fraudster access to crucial information.
Check out the following example:
2. Data Breaches
A data breach happens when a cybercriminal infiltrates a data source and extracts sensitive information. Cybercriminals find a way to access a company’s computer network to steal personally identifiable information.
When criminals gain unauthorized access to databases or systems containing personal data, they can obtain a wealth of information that can be used to assume someone’s identity. For example, let’s say a major retailer’s customer database is breached, and the hackers access customer names, addresses, social security numbers, and credit card details. Armed with this information, hackers can engage in various fraudulent activities, such as:
- Opening credit card accounts
- Making unauthorized purchases
- Applying for loans using stolen identities.
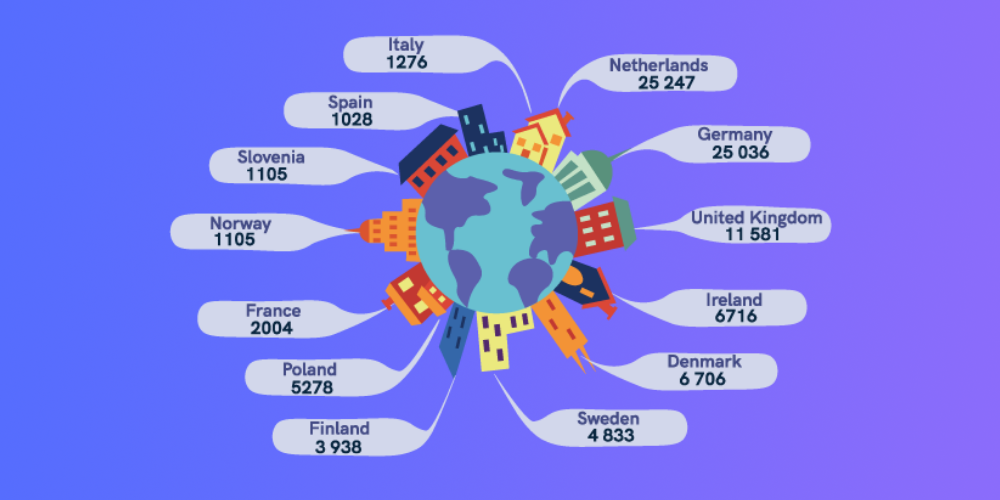
According to Statista, 25,000 data breach cases were reported in the Netherlands between May 2018 and January 2020. Check out the number of breaches in other European countries during the same period.
A few primary reasons for data breaches include:
- Weak credentials
- Software or application vulnerabilities
- Physical attacks
- User errors like improper configuration
- Third-party vulnerabilities
3. Vishing

Vishing, short for “voice phishing,” is a form of cybercrime that involves fraudulent attempts to gather personal or sensitive information from individuals over the phone. In vishing attacks, scammers impersonate legitimate organizations, such as banks, government agencies, or service providers, and use social engineering techniques to deceive victims. The aim is to get people to disclose their personal information.
The attackers use voice calls to create a sense of urgency or importance, tricking individuals into revealing confidential information like credit card numbers, passwords, social security numbers, or account details. They may employ various tactics, such as impersonating a trusted authority figure, threatening consequences for non-compliance, or offering enticing rewards to manipulate victims into disclosing their personal information.
4. Social Media Scams
Nowadays, businesses are leveraging social media to promote their services or products. Do you know the information you list on social sites can expose you to fraud? A survey conducted on 261 companies in the UK concluded that fraudsters steal crucial business information from social media sites.
Social media platforms often contain a wealth of personal information about individuals, such as:
- Full names
- Birthdates
- Location data
- Relationships
- Employment details
Imposters can exploit this information by impersonating the victim and using it to access their accounts or carry out fraudulent activities in their name. On top of that, impersonators can manipulate individuals on social media through social engineering tactics.
They might establish a rapport with someone, gain their trust, and then convince them to reveal personal information or perform actions that compromise their identity. This could include providing login credentials and financial details or even sharing scanned copies of official documents.
Related: KYC in Social Media: Less Anonymity = More Security?
5. Pharming
For those who don’t know, pharming is a kind of online fraud that involves malicious code and fraudulent websites. A cyber attacker installs malicious code on a victim’s server, which automatically directs them to a bogus site without their consent, known as DNS cache poisoning. Thus they steal your personal information, such as credit card details, personal information to commit fraud.
How to Report an Identity Theft Incident?
If you suspect that you or someone you care about has fallen victim to identity theft, it is crucial to report it as soon as possible. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) advises reporting the incident immediately at IdentityTheft.gov. This website serves as the official resource provided by the federal government, specifically for individuals who have experienced identity theft.
By reporting the incident promptly, you can initiate the necessary steps to mitigate the damage and protect yourself from further harm.
Here are the contact details:
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) online at IdentityTheft.gov or call 1-877-438-4338.
- The fraud department at your credit card issuers, bank, and other platforms where you own accounts.
- The three major credit reporting agencies. In case of identity theft, you must place fraud alerts and a credit freeze on your accounts.
How Can You Prevent Identity Theft in Practice?
There is a saying — prevention is better than cure. The majority of businesses don’t realize that weak credentials and application vulnerabilities are the primary causes of identity theft and other cyber attacks.
If you’re a business owner, naturally, you have the responsibility to ensure that your staff adheres to cybersecurity practices.
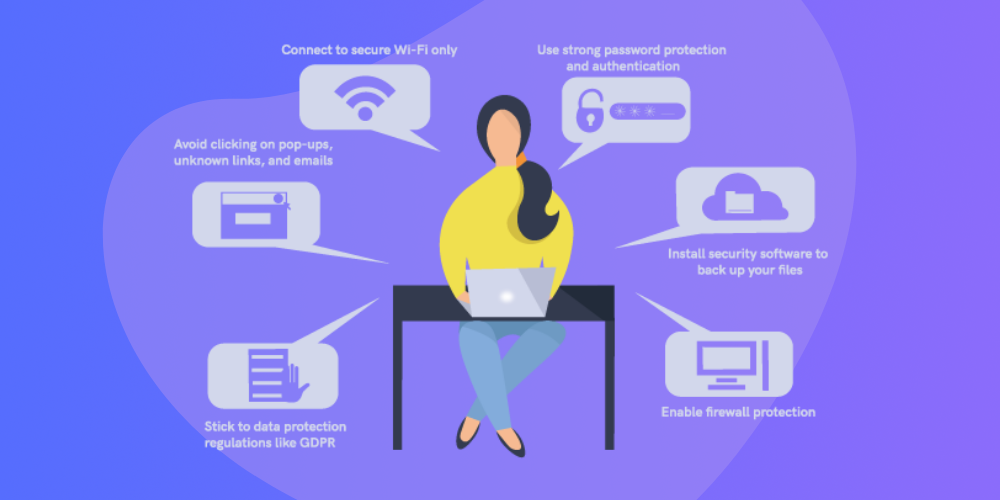
A few everyday things you can do to prevent identity theft include:
- Avoid clicking on pop-ups, unknown links, and emails.
- Connect to secure Wi-Fi only.
- Use strong password protection and authentication.
- Enable firewall protection.
- Install security software to back up your files.
- Stick to data protection regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
- Give your staff training to prevent data breaches and other unwanted consequences.
How an Automated Identity Verification Solution Helps
If you’re in a business where thousands of people use your online platform daily to buy things or use a particular service, you must implement a robust identity verification solution. It will help you identify suspicious users and stop them from using your platform for money laundering, illegal purchase, and other malicious purposes.
Look for an identity verification partner that combines face recognition, liveness detection, and ID verification in one solution to speed up the onboarding process without breaking the bank. If you’re operating in multiple countries, you must look for an identity verification solution provider that offers a cross-border solution.
iDenfy is a well-known identity verification provider that turns a customer’s device into a 24/7 ID verification terminal and face recognition system. If you want to speed up your boarding process, mitigate fraud, and meet regulatory compliance, try our all-in-one RegTech solution.
This blog post was updated on the 1st of July, 2024, to reflect the latest insights.