It can be challenging to keep up with sanctions lists that are expanding daily. On top of that, sanctions are published by various issuing bodies that don’t always align. So that leaves businesses questioning the broadening definition of what sanctions screening actually is and how to make it effective.
To overcome interpretation, management, manual data reviewing, and other challenges, our guide on sanctions screening offers some valuable intel on how to maintain Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance and conduct efficient sanctions checks.
What Does Sanctions Screening Cover?
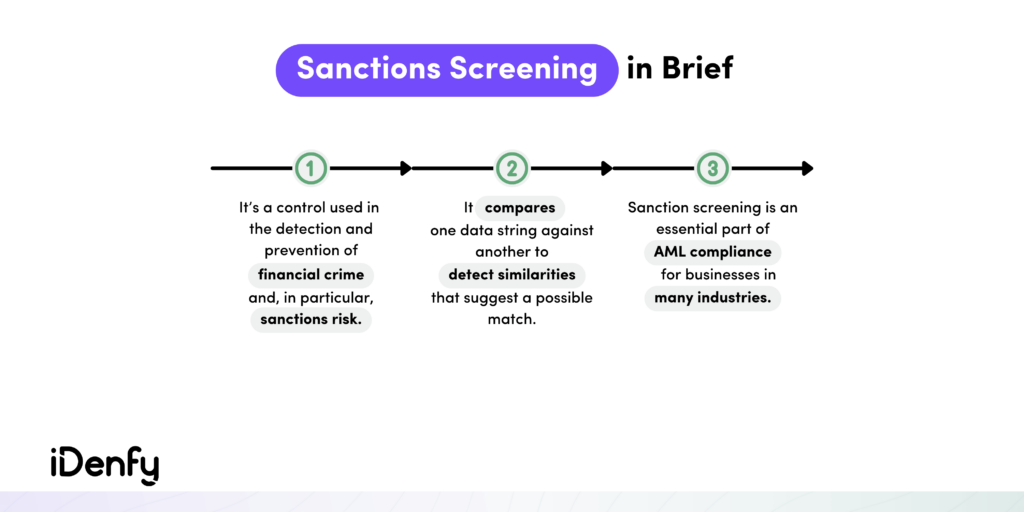
Governments impose economic sanctions to enhance national security and prevent illicit activities. Effectively managing sanctions risk requires companies to systematically assess and screen these countries, entities, and individuals against existing sanctions lists. So, with sanctions screening, the goal is to freeze assets and restrict trade with entities included in these lists.
But how can you achieve this? Sanctions screening means possessing up-to-date and accurate data, as well as conducting thorough queries across pertinent sanction lists. Regular screening is essential for ensuring ongoing compliance. That’s why obligated entities should have well-established processes in place to address situations where a country, entity, or individual emerges on a sanctions list.
What is a Sanctions List?
A sanction list is a compiled record list of individual sanctions that can be applied to:
- Individuals
- Companies
- Groups
- Countries
- States
If these entities are involved or suspected to be in illegal activity, they are put on sanctions lists.
Governments and international bodies, for instance, the European Union, allocate them to fight financial crime and maintain political diplomacy. For example, in the United States, sanctions lists are managed by different government bodies, including the Office of Financial Assets Control (OFAC), the Department of State, and others.
What is the Difference Between Manual and Automated Screening?
Companies can conduct sanctions screening manually (by entering data into an online screening tool) or through automated screening tools (by using specialized AI-powered technology). No matter the process, efficient sanctions screening should have accurate data, timely updates, and consolidated lists. Beyond customers, using automated solutions means that the company can also analyze transactions more easily and identify any involvement with sanctioned countries.
A good example of when automated sanctions screening became extremely important was after Russia’s war on Ukraine in February 2022. This led to a surge in penalties imposed on Russian entities. Given the geopolitical situation, the dynamic nature of sanctions, and the growing volume of cross-border payments, numerous firms have switched to a more robust approach to automation and compliance.
What Is Sanctions Screening in AML?
Sanctions screening in terms of AML compliance is a process that helps businesses comply with relevant regulatory rules in their jurisdiction. For example, it’s illegal for US citizens and companies to engage in business dealings with a sanctioned entity.
Remember that sanctions screening has its limitations and should be part of a larger AML program within any company.
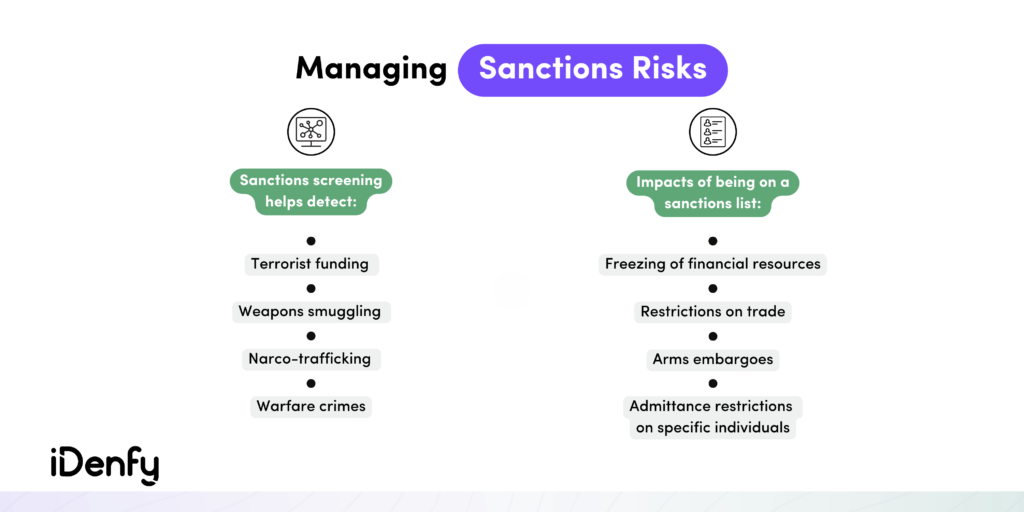
Sanctions screening is a crucial due diligence procedure in various industries such as fintech, gaming, and others. Its purpose is to prevent legal, reputational, and financial damage caused by noncompliance and involvement in illegal trade operations, money laundering, terrorist financing, and similar activities.
🖇️ Related: PEPs and Sanctions Checks Explained
What are the Main Types of Screening Controls?
Typically, companies use two key screening controls:
- Customer screening is designed to detect sanctioned individuals, entities, or organizations during the onboarding process and other stages of the customer relationship.
- Transaction screening is programmed to spot transactions that are linked to sanctions on individuals, entities, and organizations.
Despite that, sanctions are complex and come in different forms. While economic embargoes ban all transactions and activities involving a specific country, list-based or smart sanctions target specific individuals, entities, and organizations.
In contrast, secondary sanctions target third-party actors that engage in business with a specific regime, person, or organization. For instance, some Ukraine-related programs focus on Russia’s financial and energy sectors. This implies that entities not on a sanctions list but connected with a sanctioned entity can pose a risk to the related business.
Who Can Impose Sanctions?
Various entities, including governments, international organizations, and regulatory bodies, can impose sanctions:
- Governments. They can impose sanctions on other countries or specific individuals or entities within those countries, often for national security or foreign policy reasons.
- International organizations. For example, the United Nations can also impose sanctions as a means of promoting international peace and security.
- Regulatory bodies. They include financial watchdogs or law enforcement agencies that can impose sanctions on individuals or entities for violating laws or regulations related to financial crimes and illegal activities.
For example, OFAC can impose sanctions on specific individuals or geographic regions. These sanctions can include restrictions on trade, travel, or financial transactions, among other things.
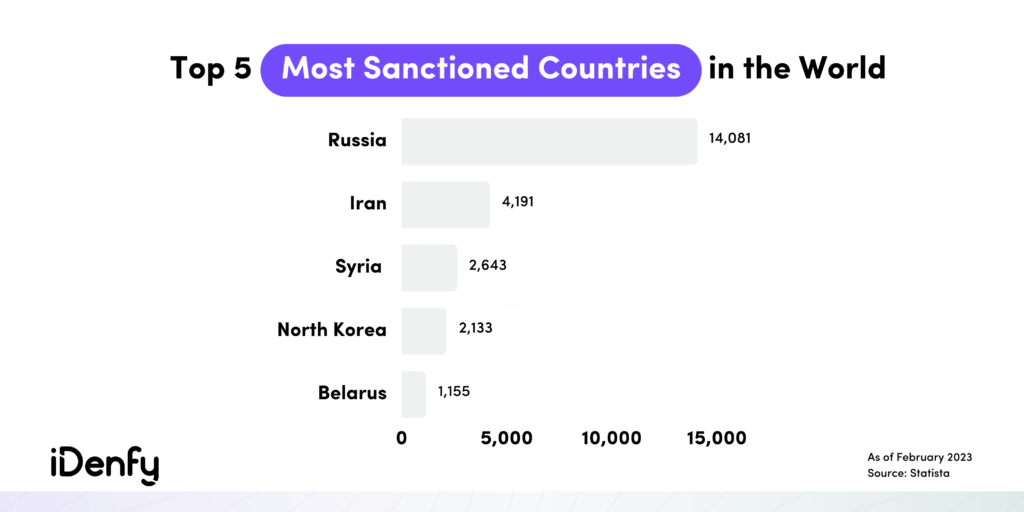
Currently, another infamous example of sanctions is the EU’s imposed sanctions against Russia in response to the war and aggression against Ukraine.
Why Do You Need Sanctions Checks?
The key question to consider is whether sanctions screening would be beneficial for your business. Smaller organizations with limited funding may not see the need since they have fewer customers and partners to monitor.
On the other hand, larger multinational companies face greater challenges in overseeing all their business partners and transactions. In such cases, implementing sanctions screening would be a smart move. This helps companies comply with regulations and prevent any unwanted business relationships.
What Is the Purpose of Sanctions Screening?
One of the main purposes for companies to implement sanctions screening is to comply with local or international jurisdictions and minimize potential risks by detecting suspicious counterparties before starting a business relationship.
Organizations also use sanctions screening as one of the steps in a larger risk-based approach strategy. That’s why sanctions checks are closely tied with Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-money Laundering (AML), and Countering Financing Terrorism (CFT) procedures.
Sanctions screening helps organizations avoid costly fines, reputational damage, and legal issues. Look at other benefits that come with sanctions checks:
- Fraud detection. Sanctions screening can help detect fraudulent transactions by cross-referencing sanctions lists. In some cases, companies may use private blacklists that contain sanctioned beneficiaries suspected of fraud.
- Financial insurance. Sanctions can lead companies to financial risks, especially when their business partners or customers are unexpectedly sanctioned. Using sanctions screening can significantly reduce these risks, helping organizations avoid doing business with sanctioned parties.
- Regulatory compliance. To maintain compliance, some regulated entities and financial institutions must conduct sanctions screening. The regulations depend on the jurisdiction in which the organization operates. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties or fines.
When Should Companies Conduct Sanctions Screening to Ensure Compliance?
After conducting an initial risk assessment, sanctions screening should be a priority when onboarding a new customer or third party. Additionally, to remain compliant with the constantly evolving sanctions landscape, organizations should regularly screen sanctions lists and their existing customers or third parties.
However, this can be a challenging task, especially when dealing with high transaction volumes. To ensure compliance with sanctions requirements, companies must find ways to overcome these challenges and implement effective sanctions screening measures.
How to Identify Relevant Sanctioning Bodies for Businesses?
To avoid potential issues, it’s essential to stay up-to-date with the latest sanctions and implement effective screening controls.
Here are the primary sanctions lists categorized by relevant sanctioning bodies and the countries, territories, partnerships, alliances, and currencies they operate within:
- The OFAC Sanctions List. OFAC applies to all US citizens and corporate entities incorporated in the US. Additionally, it applies to any entity that trades in US dollars, US goods and components, or has a US parent or affiliate.
🟩 Check the sanctions screening OFAC search tool here.
- The EU Consolidated List of Sanctions. It applies to all citizens and corporate entities that are established in a member state and are overseen by the EU Council.
🟩 Find the list of persons, groups, and entities subject to EU sanctions here.
- The HM Treasury Sanctions List. It applies to all individuals and legal entities that operate or conduct business activities within the United Kingdom, including UK nationals and legal entities established under UK law. It is enforced and overseen by the Office for Financial Sanctions Implementation (OFSI).
🟩 Check the UK Sanctions list here.
- The UN Sanctions list. This sanctions list overseen by the UN Council applies to all countries that are members of the United Nations.
🟩 Find the UN sanctions list search here.
To mitigate the risk of conducting business with prohibited parties, companies also often have their internal lists, which can be:
- Whitelists are made up of trusted parties that have already undergone KYC, such as suppliers or business partners.
- Blacklists are compromised entities that companies wish to avoid doing business with, such as fraudulent names, employees, accounts, or any other parties suspected of engaging in illicit activities.
What Are the Challenges of Sanctions Screening?
Screening for sanctions may sound straightforward, but it’s actually a challenging process that involves several differentiating factors. These include various cultures, languages, acronyms, and aliases across different jurisdictions. On top of that, organizations are facing more sophisticated sanctions evasion techniques, including the use of virtual assets.
Furthermore, Western nations are pushing to expand sanctions to cover a broader range of issues, such as human rights violations and cyberattacks. All of this is happening in the context of a rapidly changing geopolitical environment, which is making it increasingly difficult for organizations to meet their sanctions obligations.
Some common challenges businesses face are mainly related to manual screening, including:
- Lengthy processes. Screening large volumes of data manually is often insufficient, making it hard to keep up with the amount of data that needs to be screened or entered manually.
- Human errors. Flaws in screening can occur due to typos, especially for foreign entities. Additionally, incomplete, inaccurate, or outdated customer data may result in missed sanctioned individuals. Different writing systems or naming conventions, including names written in Chinese characters, Cyrillic script, or Arabic script, can make the screening more complex.
- False positives. Businesses often face false positive results or duplicates when they don’t have an effective sanctions screening system in place. For example, if a compliance officer is confident that the match is a false positive, they may whitelist the person’s name to avoid future matches.
With these factors considered, companies require trustworthy sanctions screening partners who employ modern AI technology to tackle and handle these challenges.
How to Build a Successful Sanctions Screening Process?
Sanction screening systems often fail or perform poorly due to the lack of data quality. Therefore, companies must ensure that their KYC data is collected and reviewed to prevent generating a high number of false positives and to avoid missing any sanctioned entities during the screening process.
To ensure effective sanctions screening, organizations must conduct regular and automated screening of their customers, suppliers, and transactions. This process should take place at the start of new relationships to verify the legitimacy of the relationship, followed by a regular screening at regular intervals or upon events like regulatory changes.
Here are the five most important sanctions screening practices:
- Make sure to comply with the sanctions screening regulations enforced in your jurisdictions by checking them.
- Regularly perform sanctions screening to ensure that you are aware of the most recent updates, including newly added sanctioned parties.
- Ensure that the format of your data matches the format of the sanctions screening lists. This can help reduce the number of false positives that you have to analyze.
- Make sure to review any flagged screening results and take further necessary actions to comply with sanctions regulations.
- Use automated tools for sanctions screening to ensure that screening occurs regularly. This helps avoid the need for manual data entry and reduces the time needed for analyzing screening results.
iDenfy’s Automated Sanctions Screening Software
To eliminate the hassle around sanctions checks, iDenfy offers a fully automated AML Screening solution with built-in sanctions screening checks. It enables companies to regularly screen against multiple global sanctions and watchlists, including additional protection measures, such as PEP screening.
Contact us for more details or get a free demo to see the sanctions screening software in action.




