Anti-Money Laundering or AML screening is the process of conducting necessary checks to assess whether customers are at risk of engaging in money laundering activities. It involves verifying their identities and comparing them against relevant watchlists.
AML screening is a crucial component of a bigger AML program, which encompasses transaction monitoring, risk management, and reporting of any identified suspicious activities. Together, these elements ensure a robust AML framework that’s able to prevent and detect potential money laundering incidents.
Beyond mandatory compliance requirements, screening helps ensure that your business doesn’t become a channel for money laundering and other complex financial crimes, which are getting more complex by the minute. For instance, cryptocurrencies and online banking systems have opened up new avenues for money laundering, as they offer greater anonymity and speed in transferring funds.
Let’s not forget offshore banking, complex investment structures, or layered transactions. This complexity can make it difficult for law enforcement agencies to track the true source of funds and identify suspicious patterns effectively.
Read more about the process of AML screening and how it can benefit your business.
What is the Objective of AML Screening?
The primary objective of AML screening is to detect and prevent fraudulent activities, including illegal transactions, money laundering, and terrorism financing.
This goal can be broken down into three main parts:
- Conducting risk assessments. The screening process involves evaluating the risk associated with customers and transactions to identify potential suspicious activities and high-risk customers.
- Avoiding sanctions violations. AML screening helps ensure that transactions comply with international sanctions and regulatory requirements, preventing any inadvertent involvement with sanctioned entities or countries.
- Protecting against regulatory fines. By implementing effective AML screening measures, businesses and financial institutions can safeguard themselves from potential fines and penalties imposed for non-compliance with AML regulations.
Not just sanctions lists but also other wanted lists must be checked during AML screening. High-risk customers are considered to be politically exposed persons (PEPs), which have their own lists due to being exposed to a higher risk of money laundering. PEPs have connections and can be linked to financial crimes, such as bribery and corruption.
So, in general, financial institutions and other regulated industries must conduct AML screening on their customers to 1) determine their risk level and 2) prevent doing business with risky individuals, such as sanctioned entities, PEPs, etc.
When to Conduct AML Screening?
Companies conduct AML screening right at the account opening stage of the customer onboarding process to proactively prevent fraud before it has a chance to occur.
However, there are other cases when AML screening must be performed on customers:
- During sanctions list updates. Companies must conduct AML screening whenever there are updates to sanctions lists to ensure compliance with the latest regulations and restrictions.
- When starting third-party relationships. Collaborating with third-party vendors, suppliers, or partners means that companies should perform AML screening to assess the risk associated with these external entities. Companies are also obligated to conduct AML screening for the ultimate beneficial owners (UBOs) of any firm they engage in business with.
- When dealing with large transactions. Businesses often screen and scrutinize large or unusual transactions to ensure they are legitimate and not indicative of money laundering or other illicit activities.
But risk levels change over time, turning AML screening not into a one-time thing but rather a continuous process. So even after a customer has opened an account and completed the onboarding process, the AML screening doesn’t stop.
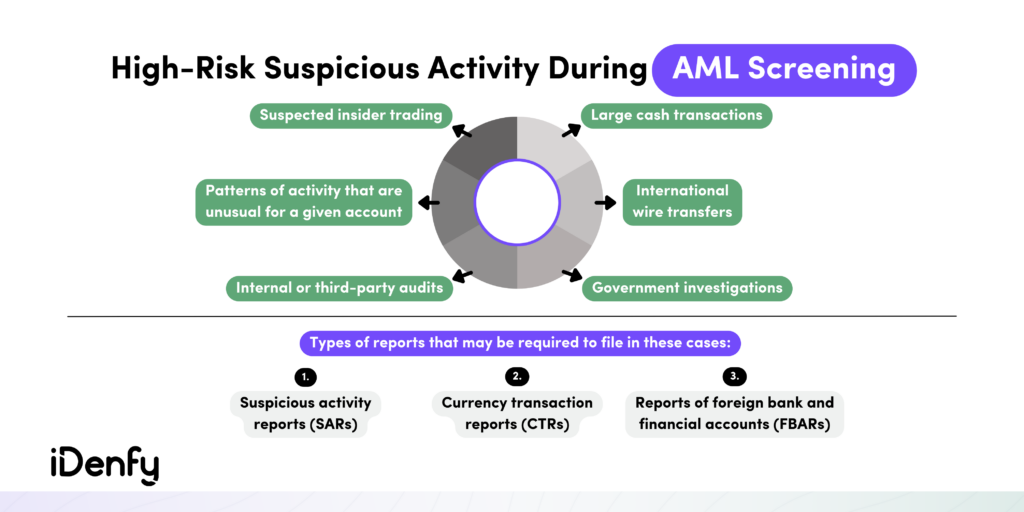
Companies need to frequently monitor customer activities and transactions to detect any suspicious behavior or changes in risk profiles over time. This helps ensure that the risk assessment remains up-to-date and aligns with any changes in the customer’s circumstances.
How Does the AML Screening Process Work?
The AML screening process works by conducting thorough checks on customers and their transactions to identify potential risks of fraud. The screening involves analyzing customer information, including verifying their identities to assess the legitimacy or suspicious nature of their behavior. In other words, AML screening aims to determine the level of risk behind a customer.
During the AML screening process, the collected and verified (through document verification, government ID verification, or other means) customer information (name, date of birth, sometimes, address, or SSN) is then cross-checked with the mentioned databases, like PEPs, sanctions lists, watchlist, and global crime lists. Additionally, adverse media screening can be used to enhance the effectiveness of the AML screening process.
Key Types of AML Screening in Practice
There are different types of AML screening processes that are crucial when creating a broader AML compliance program.
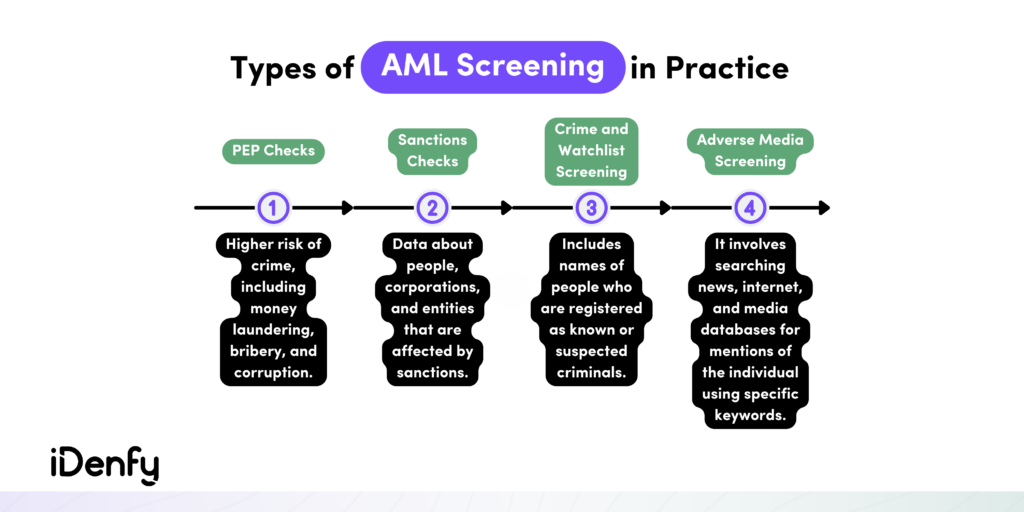
Check out the most popular practices that banks and other regulated companies include when screening their customers:
Sanctions Screening
Sanctions screening is the process of comparing a customer’s personal information with the data provided on government-issued sanctions lists. A sanctions list is a compilation of individuals, corporations, and entities subject to sanctions. Besides the person’s name, these lists frequently include additional details like aliases, date of birth, place of birth, nationality, and identification numbers.
Sanctions also refer to penalties or restrictive measures imposed by one or more governments against specific individuals or entities. While some sanctioned individuals are directly listed, others can be subject to sanctions due to their associations with these entities, such as family members or business associates. This broader scope ensures that individuals involved in illicit activities can be effectively detected and addressed, even if their names aren’t listed on sanctions lists.
PEP Screening
PEP screening is the process of identifying people with high status who are in visible positions, like the government, politics, or other public sectors. While PEP screening is vital for detecting and scrutinizing suspicious political figures, it also plays a role in helping businesses comprehend the broader risks associated with engaging with politically exposed persons.
Politically exposed persons are particularly susceptible to being targeted by money launderers through blackmail or bribes due to their prominence in the public eye. PEPs also pose a higher risk due to their association with adverse media coverage, often bringing negative attention to their associations, which can create reputational risks for businesses. So, by conducting PEP screening, companies can proactively manage potential risks and maintain the integrity of their operations and financial systems.
Adverse Media Screening
Adverse media screening, also called negative news screening, is the process of checking various news sites or media bases with the purpose of screening customers who carry a higher risk of crime. For example, if a user is attempting to open a new account at an online bank, and adverse media screening reveals that they were previously arrested for tax fraud, it’s reasonable to assume that this person presents a higher risk for engaging in similar activities.
Adverse media screening can be done manually, but nowadays, most modern institutions prefer using automated checks due to large volumes of data. Automation saves time and reduces the risk of human error. Automated adverse media checks quickly search for mentions of the individual and relevant keywords and can even help identify sanctioned entities and PEPs.
Watchlist Screening
Watchlist screening is the process of checking a person’s information against various databases containing data about known or suspected criminals. This process helps identify individuals who might be associated with illicit activities or pose potential risks to businesses and financial institutions.Watchlists are curated by law enforcement agencies, governments, international organizations, and other regulatory bodies.
You can say that watchlists share many similarities with sanctions lists, encompassing personal information such as an individual’s name, aliases, date of birth, and other important details. These lists are constantly being updated with new names, making it crucial for AML screening to prioritize up-to-date databases and preferably employ real-time screening to ensure effective due diligence.
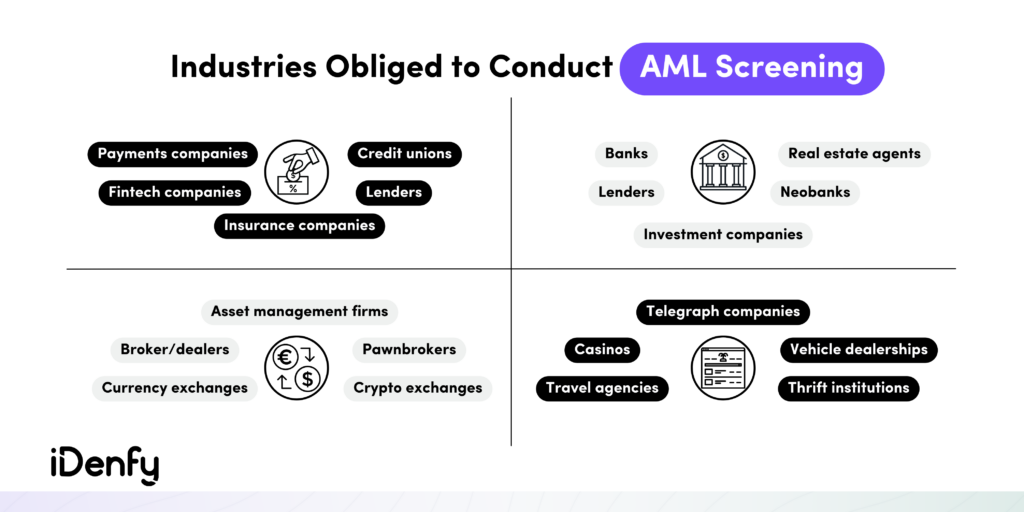
Who is Legally Required to Conduct AML Screening?
Entities deemed as financial institutions are required to perform AML screening. This includes companies that carry out financial transactions or, depending on the jurisdiction, deal with high-value items or large sums of money that may be susceptible to money laundering.
For example:
- iGaming operators
- Cryptocurrency platforms
- Real estate agencies
- High-value item dealers, such as art traders
- Banks and other financial institutions
- And more
On top of that, major market governments, for example, the US, mandate that all companies conducting business on US soil, with US entities, or involving US persons abroad must have AML frameworks in place, including robust screening processes. This requirement aims to enhance the overall integrity of the financial system and prevent illicit activities.
The Importance of Performing AML Screening
Companies that neglect AML screening not only increase their vulnerability to being targeted by money launderers but also expose themselves to potential fines, audits, and reputational damage due to their negligence. Ultimately, implementing proper AML measures means that the organization is contributing to a more secure and vigilant financial landscape, preventing illicit activities and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
How to Ensure Effective AML Screening?
With technological advancements, manual AML screening and monitoring methods are a thing of the past. With access to global regulatory databases like watchlists, PEPs, and sanctions data, AI-powered screening solutions increase the reliability of customer identity verification processes, allowing you to onboard more users in less time, safely, and in a compliant manner.
Are you interested but don’t know where to start? You’re in the right place. Try out our free demo, and check out how our AML tools perform in various industries.




