In ancient civilizations, various writing systems were developed around the world. In Europe, the modern education system originated during the High Middle Ages, and the Roman Catholic Church monasteries were the education centers. That’s why education was mainly imparted through the Buddhist and Vedic education systems.
We can confidently say that, in ancient times, most schools were based on religious values. In recent times, the purpose and way of education have changed. According to an article published in Forbes, education and technology are evolving together. Schools and universities have started adopting more technology to teach various things.
Distance education and e-learning are already trending, allowing students to study without being physically available in a school. Unfortunately, there are many challenges to this modern education system, causing threats for students and educators.
Educational institutions house extensive, sensitive personal data regarding their students, encompassing academic records and financial details. As a result, safeguarding this information from unauthorized access and misuse became a primary obligation for the education sector.
So, tag along, as this article will discuss some significant challenges of the modern education system and determine how identity verification can help enhance the e-learning landscape though secure onboarding practices and fraud prevention measures.
The Main Challenges of the Modern Education Sector
The modern education sector faces many challenges that demand our attention and concerted efforts. One of the primary challenges lies in adapting to rapidly evolving technology. With the digital revolution sweeping across industries, education must keep pace with innovative teaching methods and digital tools that can enhance learning experiences.
However, the issues in the education sector don’t end here. Tackling these challenges, head-on is essential to ensure that education remains a powerful force for personal and societal advancement in the modern world. Let’s look into it:
Data Security
According to a report by the K-12 Cybersecurity Resource Center, the ransomware attacks and data breaches in schools and colleges in the USA are three times more than what was disclosed in 2018. On the 5th of March 2020, the Icelandic SA imposed a fine of ISK 1.300.000 on the Breiðholt Upper Secondary School for the personal data breach.
Educational institutions collect and store vast amounts of sensitive student data, from personal information to academic records. Protecting this data from breaches and unauthorized access is crucial. The rise of online platforms and digital tools introduces new vulnerabilities that can lead to data leaks if not properly secured.
It wouldn’t be wrong to say that the education sector has become gainful for cyberattackers worldwide. The primary reason is that the personal data (personally identifiable information, health details, and financial data) maintained by schools about the staff and students is a hot commodity sold in millions for fraud.
Cybersecurity Threats
E-learning platforms are susceptible to cyberattacks, including phishing, ransomware, and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. These threats can disrupt learning activities and compromise the integrity of the educational process.
In addition, educational institutions must navigate various data protection laws and regulations, such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) in the United States, and ensure compliance while implementing e-learning solutions.
Recent Statistics of Cyberattacks on Students
- As per a study conducted by DarkTrace, more than 100 Singapore-based customers face 16 times more attacks on educational institutions than other retail organizations.
- In May 2020, 8Belts, a Spanish e-learning platform, experienced a data breach which affected 150,000 e-learners.
- In May 2020, another e-learning platform named OneClass suffered a data breach, which exposed the data of about one million students across North America.
- In June 2020, cybercriminals hacked the servers at the San Francisco School of Drugs, California. Attackers demanded USD 1 million to provide access to data.
Fraud detection and prevention service from market leaders. Schedule a free demo here.
Other Challenges Related to the E-Learning Sector

Limited to No Dedicated IT Resources
Most educational institutions have a shortage of dedicated IT resources to cope with cybersecurity challenges. Some institutions may operate with outdated IT infrastructure that requires significant investment to meet modern security standards. This further strains available resources.
Educational institutions have diverse IT needs, ranging from maintaining learning management systems to securing student data and research assets. This diversity can stretch already limited IT resources thin. Lastly, many educational organizations, especially smaller ones or those in underfunded areas, often have limited budgets for IT resources. This can result in insufficient funding for cybersecurity measures.
The Changing Student Lifecycle
The roles of students in an educational institute keep changing with each passing year. Students are promoted to the next standard; some become alumni, while others become teacher assistants. As a result, educational institutes need to verify and validate these new identities as soon as they transition to new positions or roles. It will minimize the risk of a security breach to a great extent.
Why Cyber Threats to the Education Sector Have Intensified?
For a long time, the education sector assumed that it didn’t have anything that cyberattackers could attract. Still, numerous schools, universities, and education systems lack the resources required to maintain a secure cybersecurity environment.
In most education facilities across the world, they don’t have a full-time staff dedicated to cybersecurity. If a few schools have dedicated cells to deal with data breaches, their employees don’t have the expertise to manage advanced cyber attacks.
Other factors influencing the higher risk of cybercrime in education include:
Remote Work and Connectivity. Educational institutions have adapted to remote work models for administrative staff, teachers, and students. This increased connectivity has expanded the attack surface, making it more challenging to secure the entire network. Cyber attackers have targeted remote employees and students through phishing attacks and malware, taking advantage of the less secure home network environments.
Valuable Data Stores. Educational institutions store vast amounts of sensitive data, including personal information, financial data, and research findings. These data stores are lucrative targets for cybercriminals seeking to steal or ransom this information.
- The proliferation of Online Learning Platforms. The shift to online learning, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, has led to a surge in the use of learning management systems (LMS) and video conferencing tools. Cybercriminals have exploited vulnerabilities in these platforms. For instance, the phenomenon of “Zoom-bombing” gained notoriety when unauthorized individuals disrupted virtual classrooms by infiltrating Zoom meetings, causing disruptions and privacy breaches.
Ensure your customers are real. Schedule a free demo here.
Some Popular Cybersecurity Threats Education Sector Faces Today
- Social engineering attacks that include phishing are on the rise in the education sector. According to statistics, in 2019, 41% of higher education breaches and cyber-attacks were caused by social engineering attacks. According to CBC News, MacEwan University was defrauded of $11.8 million after a staff member fell victim to a phishing attack.
- Ransomware attacks that involve bad actors infecting data files and systems via malicious software are another big threat to the education system.
- Using stolen identities is also a common issue. Sometimes, cybercriminals pretend to be someone else to gain access to a network and then spread Malware. This kind of attack is known as spoofing. It can happen in various ways, but attackers prefer email spoofing and caller ID spoofing. To target educational institutions, fraudsters might target IP address, DNS (Domain Name Server), or ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) services.
- Password hijacking is another standard method attackers use to gain access to the user’s login credentials. In most cases, they simply gain access by guessing common passwords such as “iloveyou,” “sunshine,” “qwerty”. A report states that 73% of people duplicate their passwords in their personal and work accounts, making it easier for hackers to steal login credentials.
- Phishing is a malware attack that tricks victims into disclosing their sensitive information, such as financial data, login credentials, and anything else that could be of high importance to hackers.
What is Student Identity Verification?
Student identity verification is the process of confirming a learner’s identity with the goal of ensuring that the person who registers for a class, for example, is the same individual who completes the coursework. Traditionally, student identity verification has been a manual process aimed at confirming a student’s identity at different points in their educational journey.
Recognizing that manual verification can be error-prone, fraudulent, and time-consuming, many institutions are now transitioning to automated verification systems. Whether for accessing on-campus resources or obtaining retail discounts, students typically scan or present their identity documents.
The Key Benefits of Identity Verification in the Education Sector
Educational institutes can benefit from identity verification in numerous ways:
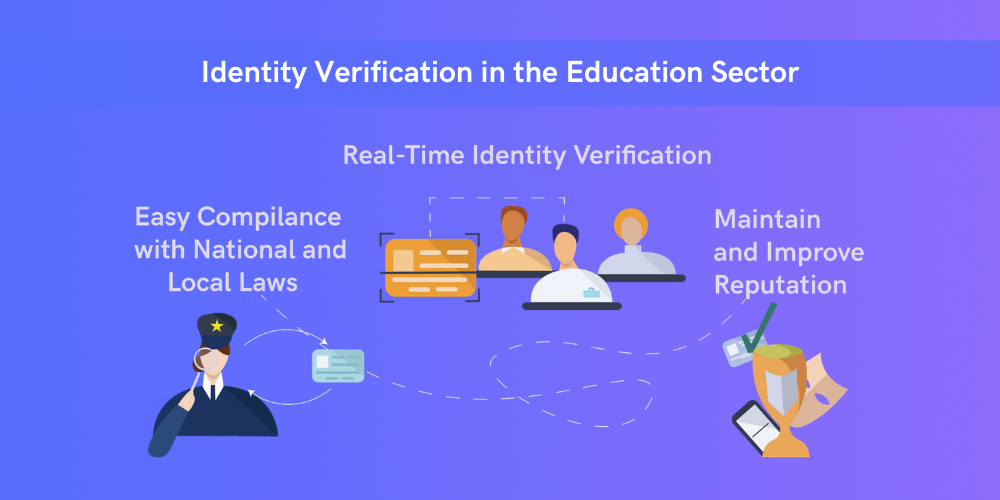
1. Real-Time Identity Verification for Increased Security
An advanced identity verification system allows institutions to verify their staff and students in real-time and eliminate the risk of ID thefts. With the help of a powerful verification system, educational institutes can conduct checks on documents like a government-issued ID, driving license, passport, or data, such as a social security number.
2. Easy Compliance with National and Local Laws
Instant yet advanced verification solutions also enable schools and universities to comply with local and national identity verification requirements.
3. Maintained and Improved Reputation
Not having a proper identity verification system increases identity fraud risk and is a bad sign for an institution’s reputation. According to a recent report, half of the hacked businesses struggle to attract new customers.
If you’re searching for an AI-enabled remote identity verification solution for your school, college, or any other educational institute, you can try iDenfy.
We combine liveness detection, ID verification, and face recognition in a single solution to provide a powerful verification solution. To know more, book a meeting.
This blog post was updated on the 7th of June, 2024, to reflect the latest insights.